As of my last update in September 2021, Bacillus megaterium is a species of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria that belongs to the Bacillus genus. It is known for its large size among the Bacillus species and has been extensively studied due to its significant biotechnological potential and diverse applications. Here is a comprehensive overview of Bacillus Megaterium based on the information available up to September 2021:

Taxonomy and Morphology:
Bacillus Megaterium is a member of the phylum Firmicutes, class Bacilli, order Bacillales, and family Bacillaceae. The species name “megaterium” is derived from the Greek words “mega” (large) and “terion” (little animal), referring to its relatively large size compared to other Bacillus species. It appears as Gram-positive, endospore-forming, and rod-shaped bacteria.
Habitat and Distribution:
Bacillus Megaterium is a versatile bacterium found in various environments, including soil, water, air, and decaying organic matter. It is considered ubiquitous and can thrive in different ecological niches.
Biotechnological Applications:
Bacillus Megaterium has gained considerable attention in biotechnology due to its robust characteristics and the ability to produce various enzymes and metabolites with industrial relevance. Some of its applications include:
- a. Enzyme Production: Bacillus Megaterium can produce several enzymes, such as amylases, proteases, lipases, cellulases, and xylanases, which are valuable in industries like food, detergent, textile, and biofuel production.
- b. Biocontrol Agent: Some strains of Bacillus Megaterium have shown potential as biocontrol agents, helping to suppress plant diseases by inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms.
- c. Bioremediation: The bacterium can play a role in bioremediation processes by degrading pollutants, such as hydrocarbons and heavy metals, from contaminated environments.
- d. Protein Expression System: Bacillus Megaterium is used as a host for heterologous protein expression due to its ability to secrete recombinant proteins in large quantities.
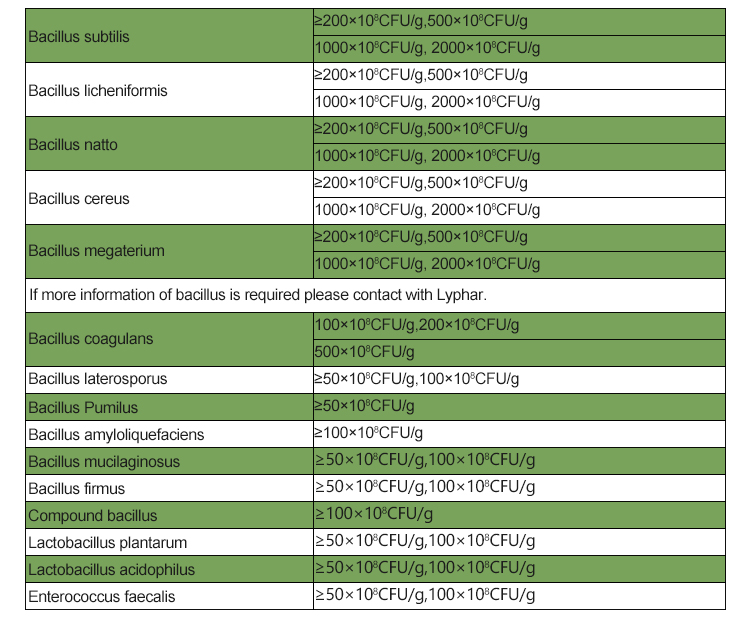
Genetic and Genomic Features:
Bacillus Megaterium has a relatively large genome, typically consisting of a single circular chromosome. The genome encodes numerous genes associated with various metabolic pathways and adaptive functions, contributing to its wide range of applications.
Research and Studies:
Numerous research studies have focused on understanding the biology, genetics, and biotechnological potential of Bacillus Megaterium. Scientists have investigated its gene regulation, stress responses, spore formation, and interactions with other organisms. Additionally, genetic engineering and synthetic biology techniques have been employed to improve its performance for specific applications.
It is essential to note that research in the field of microbiology is continuously evolving, and new findings might have emerged after my last update in September 2021. To obtain the most current and comprehensive information on Bacillus Megaterium, I recommend referring to scientific journals, research papers, and databases available beyond that date.
评论
发表评论