Coenzyme Q10, also known as CoQ10, is a naturally occurring antioxidant found in the cells of your body. It plays a vital role in energy production and is believed to have various health benefits. If you want to use Coenzyme Q10 for the best results, here are some guidelines:

Consult with a Healthcare Professional:
Before starting any new supplement regimen, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or registered dietitian. They can evaluate your specific health needs, recommend an appropriate dosage, and ensure it won’t interact with any medications or conditions you may have.
Choose the Right Form and Dosage:
Coenzyme Q10 supplements come in various forms, including ubiquinone and ubiquinol. Ubiquinol is the reduced form of Coenzyme Q10 and is often considered more bioavailable. Your healthcare provider can help you decide which form is best for you and recommend an appropriate dosage.
Consider Your Goals:
Coenzyme Q10 is used for various purposes, such as improving heart health, boosting energy, and reducing the side effects of certain medications. Clearly define your goals for taking Coenzyme Q10 to determine the most suitable dosage and duration.
Take with Fat:
Coenzyme Q10 is fat-soluble, meaning it is better absorbed when taken with a meal that contains healthy fats. This can enhance its bioavailability and effectiveness.
Be Consistent:
To experience the full benefits of Coenzyme Q10, take it consistently as directed by your healthcare provider. Skipping doses or taking it sporadically may limit its effectiveness.
Monitor for Side Effects:
Coenzyme Q10 is generally considered safe when used as directed. However, some people may experience side effects such as digestive upset or insomnia. If you notice any adverse effects, consult your healthcare provider.
Give It Time:
Coenzyme Q10 supplements may take several weeks to months to produce noticeable results, especially for conditions like heart health. Be patient and continue taking it as recommended.
Consider Food Sources:
Coenzyme Q10 is naturally present in small amounts in certain foods, such as organ meats, fish, and whole grains. Including these foods in your diet can help support your Coenzyme Q10 levels.
Monitor Your Health:
Keep track of how you feel and any changes in your health while taking Coenzyme Q10. Share this information with your healthcare provider during follow-up appointments to assess its impact.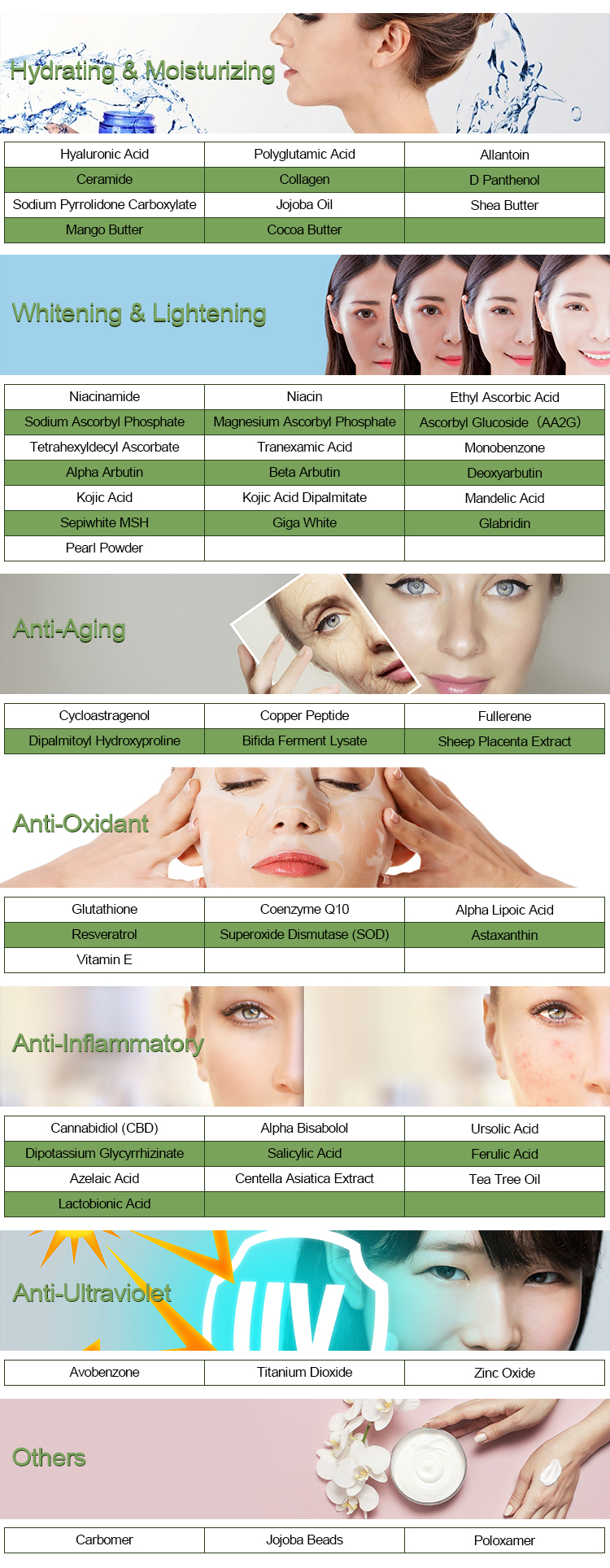
Avoid Self-Diagnosis and Self-Treatment:
Coenzyme Q10 is not a cure-all, and its benefits may vary from person to person. It’s essential to use it as part of a comprehensive health plan developed with the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Remember that Coenzyme Q10 is a dietary supplement, and it should not replace any prescribed medications or medical treatments. Always follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for the best results and safety.
评论
发表评论