Fisetin is a natural flavonoid compound found in various fruits and vegetables, including strawberries, apples, onions, and cucumbers. It belongs to the flavonol subgroup of flavonoids and is known for its potential health benefits due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Chemical Structure of Fisetin:
The chemical structure of fisetin can be represented using its molecular formula, which is C₁₅H₁₀O₆. Here’s a simplified representation of its structure:
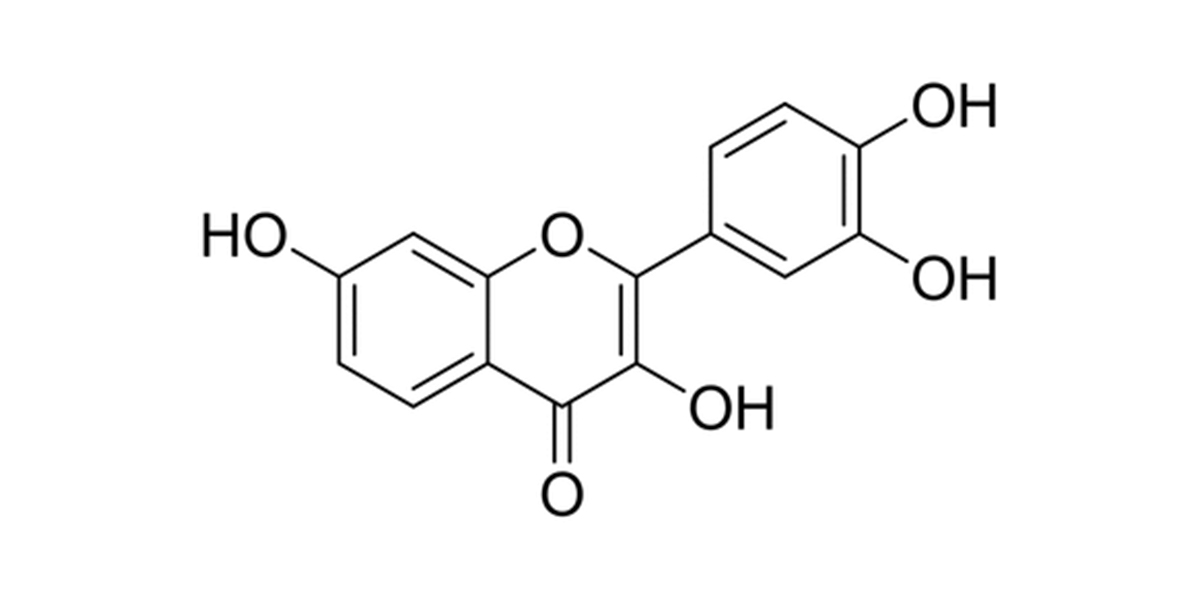
Physical Properties of Fisetin:
Fisetin possesses several physical properties that contribute to its characteristics:
- Molecular Weight: The molecular weight of fisetin is approximately 286.24 g/mol.
- Melting Point: Fisetin has a melting point around 330°C (626°F), but this can vary depending on the source and purity of the compound.
- Solubility: Fisetin is sparingly soluble in water, which means it dissolves only to a limited extent. It is more soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, methanol, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Color: Fisetin is a yellow crystalline solid, and its natural occurrence in fruits and vegetables contributes to their characteristic colors.
- UV-Vis Absorption: Fisetin exhibits UV-Vis absorption peaks in the ultraviolet and visible range, which is typical for flavonoids. These absorption properties are related to its antioxidant capabilities.
- Stability: Fisetin can be sensitive to factors such as light, heat, and oxygen. It can degrade under certain conditions, which is important to consider when storing or formulating products containing fisetin.
Bioactivity:
Fisetin’s potential health benefits stem from its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It is believed to contribute to cellular health by neutralizing harmful free radicals and reducing oxidative stress. Fisetin has also shown potential in various studies for its effects on brain health, longevity, and other aspects of human health. However, further research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and therapeutic applications.
Remember that the properties and potential benefits of fisetin may be subject to ongoing research and discoveries beyond my last knowledge update in September 2021. Always consult reliable and up-to-date sources for the latest information
评论
发表评论