Adenosine Triphosphate, commonly known as ATP, is a molecule that serves as the primary energy currency in living organisms. It plays a crucial role in energy transfer within cells and is considered the “molecular unit of currency” for cellular energy. ATP is found in all forms of life and is essential for various biological processes.
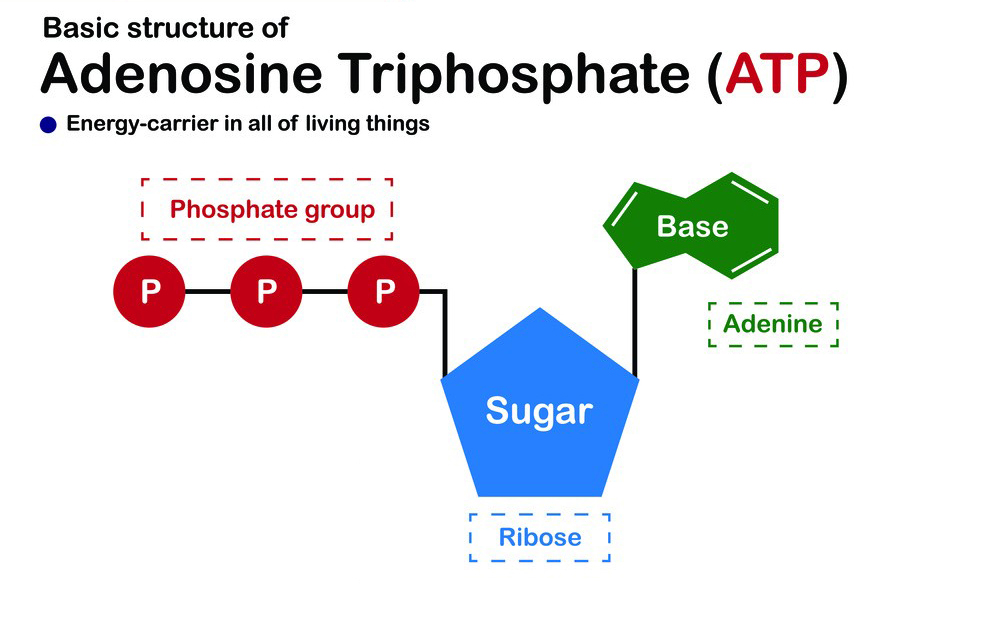
The structure of ATP consists of three main components:
1.Adenosine: This is a nitrogenous base composed of adenine, a purine base, and ribose, a five-carbon sugar.
2.Triphosphate: Attached to the ribose sugar are three phosphate groups, hence the name “tri-” phosphate. These phosphate groups are linked together by high-energy bonds.
The high-energy bonds between the phosphate groups are what make ATP an excellent energy carrier. When one of these phosphate bonds is broken through hydrolysis, a considerable amount of energy is released, providing energy for cellular processes.
The ATP-ADP cycle is the central mechanism for energy transfer within cells. When energy is required for cellular work, ATP releases one of its phosphate groups, becoming adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and releasing energy. The energy-requiring reactions in the cell can then use this released energy. Subsequently, ADP can be converted back to ATP by replenishing the phosphate group using energy derived from various cellular processes, such as cellular respiration.
ATP is involved in various cellular processes, including muscle contraction, active transport of molecules across cell membranes, synthesis of macromolecules, and many other energy-dependent reactions necessary for maintaining life.
What is potential Benefits of Adenosine Triphosphate?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a vital molecule found in all living organisms and serves as the primary energy carrier within cells. Its benefits are numerous and fundamental to various cellular processes and overall health. Some potential benefits of ATP include:
1.Energy production: ATP is often referred to as the “energy currency” of cells. When ATP is broken down into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi), energy is released and used to fuel various cellular activities, such as muscle contraction, nerve transmission, and biosynthesis.
2.Cellular metabolism: ATP plays a central role in cellular metabolism. It provides the necessary energy for anabolic processes that build complex molecules from simpler ones and catabolic processes that break down complex molecules into simpler ones, releasing energy in the process.
3.Muscle function: ATP is crucial for muscle contraction and relaxation. When muscles contract, ATP is broken down to provide energy, and when muscles relax, ATP is used to transport calcium ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum, preparing the muscles for the next contraction.
4.Nerve function: ATP is involved in nerve transmission. It helps maintain the ion gradients across nerve cell membranes, which are essential for generating action potentials and transmitting signals along nerves.
5.Active transport: Many cellular processes, such as the transport of ions and molecules across cell membranes, require energy to overcome concentration gradients. ATP powers these active transport processes, ensuring the proper functioning of cells.

6.DNA replication and repair: ATP is necessary for DNA replication, providing energy to enzymes involved in unwinding the DNA double helix and synthesizing new strands during cell division. It is also utilized in DNA repair mechanisms.
7.Enzyme activation: ATP is used to activate certain enzymes by transferring a phosphate group to them. This process, called phosphorylation, is critical for regulating enzyme activity and many cellular processes.
8.Maintenance of cellular integrity: ATP helps maintain the integrity of the cell membrane through the activity of ATP-dependent ion pumps. These pumps regulate the ion concentration inside and outside the cell, ensuring proper cell function and osmotic balance.
9.Signal transduction: ATP participates in various signaling pathways within cells. It can be released outside the cell to act as an extracellular signaling molecule or modulator of cell-to-cell communication.
Overall, the benefits of ATP are fundamental to life, and without this essential molecule, cellular processes and organismal functions would not be able to occur.
评论
发表评论